WHAT IS THE ICSI METHOD IN SURROGACY?
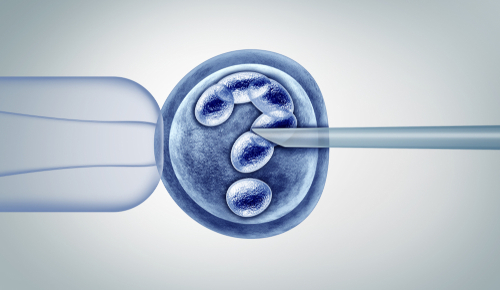
In a healthy state, a man's sperm capable of fertilisation should contain 20 million semen (minimum). Under these conditions, the probability of conception is optimal. If the concentration of biomaterial begins to decline, we can talk about pathological abnormalities and, therefore, the need for intracytoplasmic injection (hereinafter referred to as ICSI). This is the name given to the procedure of introducing a sperm cell into the egg cytoplasm during IVF and surrogacy programmes. Currently, the method is up to 100% effective - pregnancy can be achieved even in cases of severe infertility when conceiving naturally is not possible.
Indications for ICSI
- Reduced concentration and motility of spermatozoa;
- Use of spermatozoa after cryopreservation;
- Use of spermatozoa obtained by surgery;
- The presence of a high number of cells with abnormalities;
- The presence of anti-sperm antibodies (ASATs) in the ejaculate;
- A list of supplementary services (information services, translation services, nurse, babysitter, psychologist);
- Failed IVF or surrogacy programmes in the past.
A female factor can also be considered as an indication for ICSI: low fertilisation rate of oocytes, immunological reaction of the woman's body to the man's sperm, infertility of unclear pathogenesis, etc.
How does the procedure work?
Stage one. As part of the ICSI preparation, the couple undergoes an examination. The woman is offered an examination by a gynaecologist, an ultrasound investigation, a blood test for STDs, sex hormone levels and the presence of antibodies to infections. The man is offered a spermogram, a MAR-test and a urethral smear. Both partners have to be tested for genetic diseases.
Stage two. The next step is egg retrieval and purification (by puncture under sedation anaesthesia). The woman will first undergo hormonal treatment. The oocyte (one or more) is placed in a specific cup with a culture medium that simulates the internal environment of the body.
Stage three. This is when the spermatozoa are prepared for fertilisation. The man takes seminal fluid. Subsequently it is processed, placed under a microscope, the healthiest and most viable cells are selected.
Stage four. In the last stage, fertilisation takes place using ICSI. The oocyte is fixed, its membrane is pierced with a micro-needle and sperm is injected into the cytoplasm. The biological material is put in a medium where the cell division occurs, and the process of embryo formation begins. After 16-20 hours it will be clear if the procedure was efficient or not. If fertilisation is established, the embryo develops for 5-6 days and is transferred to the uterus.
How does the ICSI method differ from PICSI?
During the ICSI an embryologist selects sperm by himself based on their physical appearance. The PICSI method is used when it is impossible to evaluate the potential of the cells at first glance. To achieve this, the doctor carries out a molecular analysis. The spermatozoa are extracted from the seminal fluid and placed in a sterile cup, after which hyaluronic acid is added. Healthy cells begin interacting with the substance, indicating their high fertility.
The ICSI method belongs to ART and is successfully used in our surrogacy agency. We offer our European clients a lot of advantages: supreme level of service, compliance with international protocols, unique system of biomaterial quality control, professionalism of doctors, our own equipped laboratory, etc. By entrusting your health to us, you will be satisfied with the result!
Interesting! For the first time the method of ICSI conception was implemented in 1992 - an absolutely healthy child was born after only 9 months.

Any questions?


Any questions?
I'm Kate, the agency's director.
Leave your email or phone, and we will send you our presentation with prices.